1 清华大学精密仪器系精密测试技术与仪器国家重点实验室,北京 100084
2 北京邮电大学电子工程学院信息光子学与光通信全国重点实验室,北京 100876
在光纤锁模激光器中,模式相位锁定产生周期短脉冲的过程称为锁模过程,产生的脉冲在广义上被称为“光耗散孤子”。光纤锁模激光器从传统的单模光纤锁模激光器发展到了多模光纤锁模激光器,锁模机理从一维(1D)时域耗散孤子锁模发展到了(3+1)维时空耗散孤子锁模。通过深入理解耗散孤子的产生机理,有望进一步推动光纤锁模激光器在科学和应用领域的发展,为更多领域带来更多创新和可能性。首先介绍单模光纤锁模激光器中的一维时域耗散孤子锁模,探讨不同色散区域中时域耗散孤子的产生机理;随后介绍多模光纤锁模激光器中时空耗散孤子的最新研究成果,讨论模间色散的补偿方法,揭示其丰富的时空锁模机理和潜在的应用场景;最后对光纤锁模激光器的发展前景进行展望。

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments, Department of Precision Instruments, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 Center for Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Research and Development Center for Solid State Lighting, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
Transient thermal instability represents a significant challenge in generating soliton microcombs. Fast laser sweep can be an efficient method to mitigate thermal instability, but it requires an ultrahigh laser sweep rate for crystalline microresonators with fast thermal relaxation. Here, we engineer a laser sweep waveform to generate AlN-on-sapphire soliton microcombs with an intermediate sweep speed (). Two laser sweep methods with backward plus forward tuning or two-step backward tuning added after the fast forward laser sweep were demonstrated to stabilize solitons. Reducing the soliton number is found to be useful to stabilize solitons in fast laser sweep. The effectiveness of the methods was numerically verified. Our measurements and simulations also reveal the impacts of different thermal relaxation processes occurring at quite different time scales on thermal instability. The requirement of the laser sweep protocols is discussed.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(8): A10

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Tsinghua University, State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments, Department of Precision Instrument, Beijing, China
2 Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Key Laboratory of Nanodevices and Applications, Suzhou, China
Optical metasurfaces are endowed with unparallel flexibility to manipulate the light field with a subwavelength spatial resolution. Coupling metasurfaces to materials with strong optical nonlinearity may allow ultrafast spatiotemporal light field modulation. However, most metasurfaces demonstrated thus far are linear devices. Here, we experimentally demonstrate simultaneous spatiotemporal laser mode control using a single-layer plasmonic metasurface strongly coupled to an epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) material within a fiber laser cavity. While the geometric phase of the metasurface is utilized to convert the laser’s transverse mode from a Gaussian beam to a vortex beam carrying orbital angular momentum, the giant nonlinear saturable absorption of the ENZ material enables pulsed laser generation via the Q-switching process. The direct integration of a spatiotemporal metasurface in a laser cavity may pave the way for the development of miniaturized laser sources with tailored spatial and temporal profiles, which can be useful for numerous applications, such as superresolution imaging, high-density optical storage, and three-dimensional laser lithography.
spatiotemporal control metasurface epsilon-near-zero strong coupling Advanced Photonics
2023, 5(2): 026002
清华大学 精密仪器系 精密测量技术与仪器国家重点实验室,北京 100084
光学孤子是指一种通过非线性折射率势阱维持脉冲形状不变的光波,它广泛存在于光纤、飞秒激光器、参量振荡器等系统中。近年来,人们在相干泵浦下的高Q值微腔中也观测到了光孤子,这为研究光孤子性质提供了新的实验平台。又因为微腔光孤子在频域上对应高重频的光学频率梳,微腔光孤子的诞生也极大地推动了小型化光学频率梳的发展。微腔光孤子频率梳已经可以实现自参考锁定;这使得片上集成的光频合成器、光原子钟、波分复用光源、微腔光谱仪、微腔激光雷达等众多应用成为了可能。文中介绍了微腔光孤子的产生基础,特别是光孤子相互作用相关的研究,还讨论了基于微腔的双光梳测量在高速成像与中红外气体光谱分析上的应用。
光孤子 相干泵浦 微腔光频梳 双光梳测量 optical soliton coherent pump microcomb dual-comb measurements 红外与激光工程
2022, 51(5): 20220271

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments, Department of Precision Instruments, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, School of Electronic Engineering, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
3 School of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Hainan Normal University, Haikou 571158, China
4 e-mail: xsxiao@bupt.edu.cn
5 e-mail: cxyang@tsinghua.edu.cn
Spatiotemporal mode locking is a nonlinear process of multimode soliton self-organization. Here the real-time buildup dynamics of the multiple solitons in a spatiotemporal mode-locked multimode fiber laser are investigated, assisted by the time-stretch technique. We find that the buildup processes are transverse mode dependent, especially during the stages of relaxation oscillation and -switching prior to multiple soliton formation. Furthermore, we observe that the transverse modal composition of these generated pulses among the multiple solitons can be different from each other, indicating the spatiotemporal structure of the multiple soliton. A simplified theoretical model based on pulse energy evolution is put forward to interpret the role of 3D saturable absorber on spatiotemporal structures of spatiotemporal mode-locking multiple solitons. Our work has presented the spatiotemporal nonlinear dynamics in multimode fiber lasers, which are novel to those inside the single transverse mode fiber lasers.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(10): 10001898
1 清华大学精密仪器系精密测试技术与仪器国家重点实验室, 北京 100084
2 北京邮电大学电子工程学院信息光子学与光通信国家重点实验室, 北京 100876
双光梳光谱技术作为一种新兴的宽带光谱测量技术,具有超高分辨率、高灵敏度和高采样率的特点,在气体吸收谱测量、温室气体排放监控、非线性光谱成像等领域具有重要应用。研究表明,仅从一台激光器中产生高相干的双光梳光源,克服了传统双光梳光源产生方法中存在的频率锁定系统复杂、梳齿数量较少、制作工艺困难等缺点,这种光源是理想的双光梳光源之一。结合国内外相关研究进展,综述了单腔双光梳的产生方法、单腔双光梳锁模光纤激光器中的孤子动力学研究以及单腔双光梳的应用。
激光器 双光梳光谱技术 单腔双光梳 锁模光纤激光器 中国激光
2021, 48(15): 1501001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments, Department of Precision Instruments, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, School of Electronic Engineering, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
3 e-mail: xsxiao@bupt.edu.cn
4 e-mail: cxyang@tsinghua.edu.cn
We report experimental observation of multimode -switching and spatiotemporal mode locking in a multimode fiber laser. A typical steady -switching state is achieved with a 1.88 μs pulse duration, a 70.14 kHz repetition rate, and a 215.8 mW output power, corresponding to the single pulse energy of 3.08 μJ. We find weak spatial filtering is essential to obtain stable -switched pulses, in contrast to the relatively stronger spatial filtering for spatiotemporal mode locking. Furthermore, a reversible transition process, as well as a critical bistable state, between multimode -switching and spatiotemporal mode locking, is achieved with specific spatial coupling and waveplates sets. We believe the results will not only contribute to understanding the complicated nonlinear dynamics in multimode, fiber-based platforms, but also benefit the development of promising high-pulse energy lasers.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(4): 04000530

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments, Department of Precision Instruments, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
Particle-like structures of solitons, as a result of the balance between dispersion and nonlinearity, enable remarkable elastic and inelastic soliton collisions in many fields. Despite the experimental observation of temporal vector-soliton collisions in birefringent fibers, collision dynamics of vector solitons in fiber lasers have not been revealed before, to the best of our knowledge. Here, the real-time spectral evolutions of vector solitons during collisions in a dual-comb fiber laser, which generates vector solitons with slightly different repetition rates, are captured by a time-stretch dispersive Fourier transform technique. We record the whole process of vector-soliton collisions, including the formation of weak pulses induced by cross-polarization coupling, opposite central wavelength shifts of both vector solitons, distinct intensity redistribution and dissipative energy, and gradual recovery to initial states. Furthermore, extreme collisions with strong four-wave mixing sidebands are observed by virtue of coherent coupling between the orthogonal polarization components of vector solitons. Numerical simulations match well with the experimental observations. The experimental and numerical evidences of vector-soliton collision dynamics could give insight into the understanding of nonlinear dynamics in fiber lasers and other physical systems, as well as the improvement of laser performance for application in dual-comb spectroscopy.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(3): 03000289
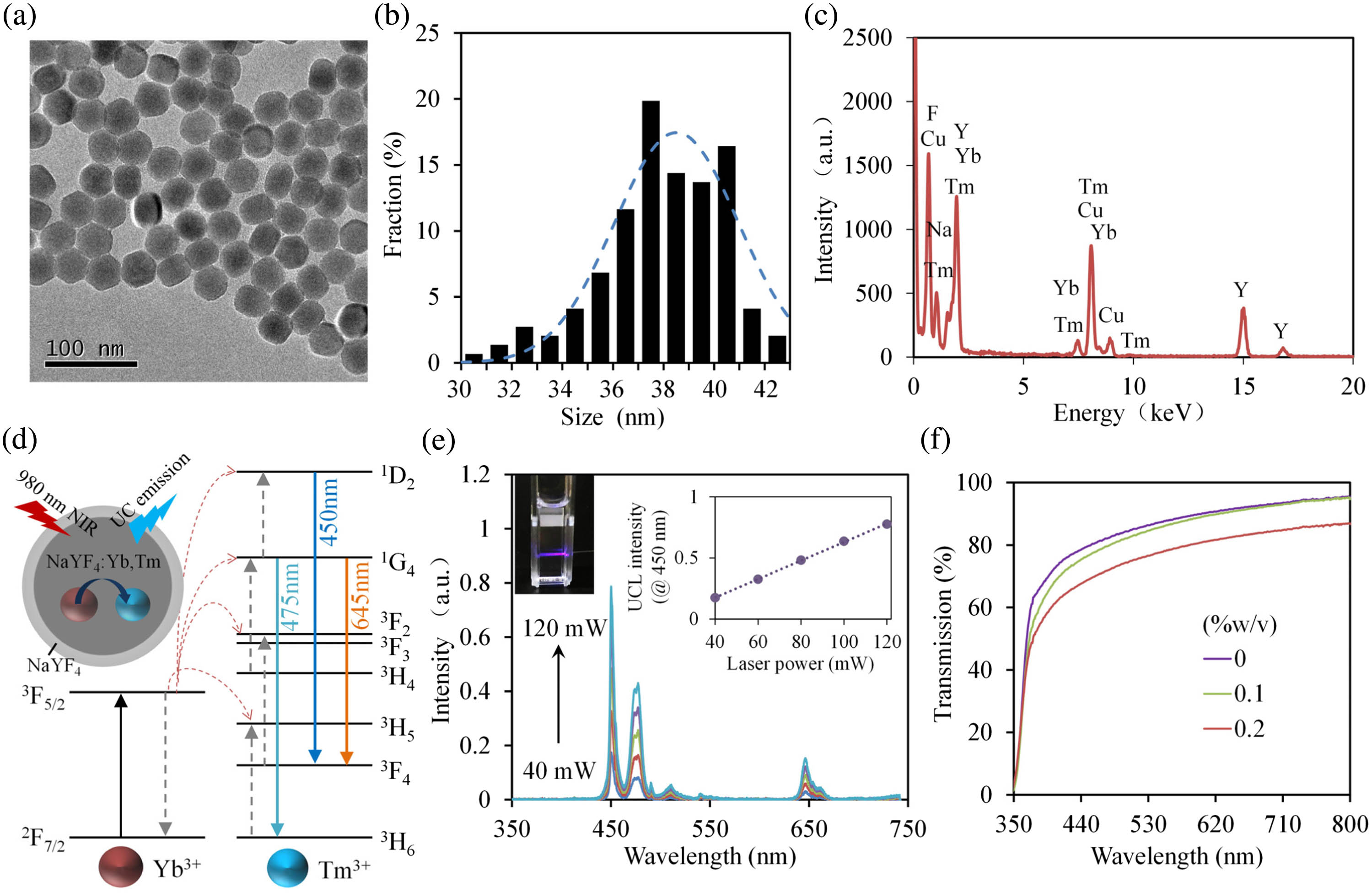
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments, Department of Precision Instrument, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 e-mail: guojj018@tsinghua.edu.cn
Dopamine (DA), as a neurotransmitter in human brain, plays a crucial role in reward motivation and motor control. An improper level of DA can be associated with neurological disorders such as schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. To quantify DA, optical DA sensors have emerged as an attractive platform due to their capability of high-precision and label-free measurement, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. However, the lack of selectivity, limited biocompatibility, and complex fabrication processes are challenges that hinder their clinical applications. Here, we report a soft and biocompatible luminescent hydrogel optical sensor capable of recognizing and quantifying DA with a simple and compact interrogation setup. The sensor is made of a hydrogel optical fiber (HOF) incorporated with upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs). DA molecules are detected through the luminescence energy transfer (LET) between the UCNPs and the oxidation products of DA, while the light-guiding HOF enables both excitation and emission collection of the UCNPs. The hydrogel sensor provides an optical readout that shows a linear response up to 200 μmol/L with a detection limit as low as 83.6 nmol/L. Our results show that the UCNP-based hydrogel sensor holds great promise of serving as a soft and biocompatible probe for monitoring DA in situ.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(11): 11001800

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments, Department of Precision Instruments, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 Laboratoire ICB UMR 6303 CNRS, Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté, F-21078 Dijon Cedex, France
We investigate numerically the pattern formation in 2-μm thulium-doped Mamyshev fiber oscillators, associated with the dissipative Faraday instability. The dispersion-managed fiber ring oscillator is designed with commercial fibers, allowing the dynamics for a wide range of average dispersion regimes to be studied, from normal to near-zero cavity dispersion where the Benjamin–Feir instability remains inhibited. For the first time in the 2-μm spectral window, the formation of highly coherent periodic patterns is demonstrated numerically with rates up to . In addition, irregular patterns are also investigated, revealing the generation of rogue waves via nonlinear collision processes. Our investigations have potential applications for the generation of multigigahertz frequency combs. They also shed new light on the dissipative Faraday instability mechanisms in the area of nonlinear optical cavity dynamics.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(11): 11001287





